
While metals such as zinc, aluminium, magnesium, calcium, etc. This is the reason why platinum and gold don’t get corrode easily and don’t form oxides.

Metals from copper to platinum are highly unreactive and don’t react with any other substance in normal conditions. While metals from magnesium to lead can react with acids. Through the reactivity series, we can tell which metal will displace the other metal.Metals from potassium to calcium are highly reactive and even react with water. In displacement reactions, a more reactive metal displaces a lesser reactive metal from its salt.
#Reactivity series series
The reactivity series has two important uses-in displacement reaction and reaction between metals and water. Study about the Development of Periodic Table here Importance of Reactivity Series \(H^+\) (Non-Metal, Reference for Comparison) Some properties of the reactivity series are as follows: The reactivity series helps in displacement reaction and reaction between metals and water. Study more about Emulsions & Suspensions here. The more easily a non-metal gains electrons, the more active it is, and is higher in the reactivity series.

The reactivity of a non-metal depends upon its capacity to add electrons in the solution state to produce positive ions. During displacement reactions, a higher active non-metal displaces a lesser active non-metal from a compound. Like metals, non-metals can also be arranged in terms of their reactivity.

The reactivity series of elements such as metals and non-metals have been discussed in the pointers below: Similarly, the reactivity series of non-metals is the series in which we arrange non-metals in the decreasing order of their chemical activity. Whereas, the metal with the highest reactivity is placed at the top of the chart. Therefore, the metal showing the least reactivity is placed at the bottom of the reactivity series chart. The reactivity series, also known as the activity series, is the arrangement of metals in decreasing order of their reactivity. Let’s find out the reactivity series of elements such as metals, non-metals, and properties and the importance of reactivity series along with reactivity series mnemonics further in this article. However, in a reactivity series, these elements are placed according to a descending order of their reactivity.
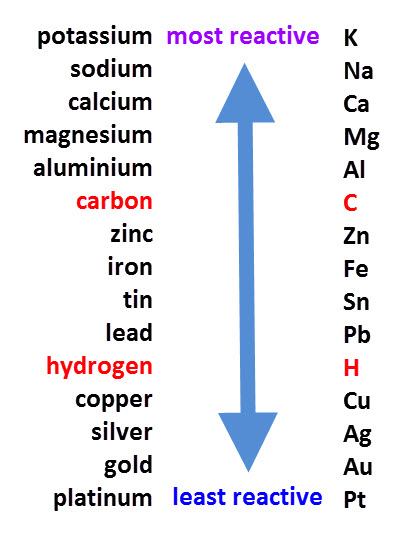
These elements are placed in the table according to their respective atomic number, irrespective of how reactive they are. Elements in the periodic table are divided into two major categories i.e metals and non-metals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
